Practical Motor Selection for Automated and Heavy Duty Workflows
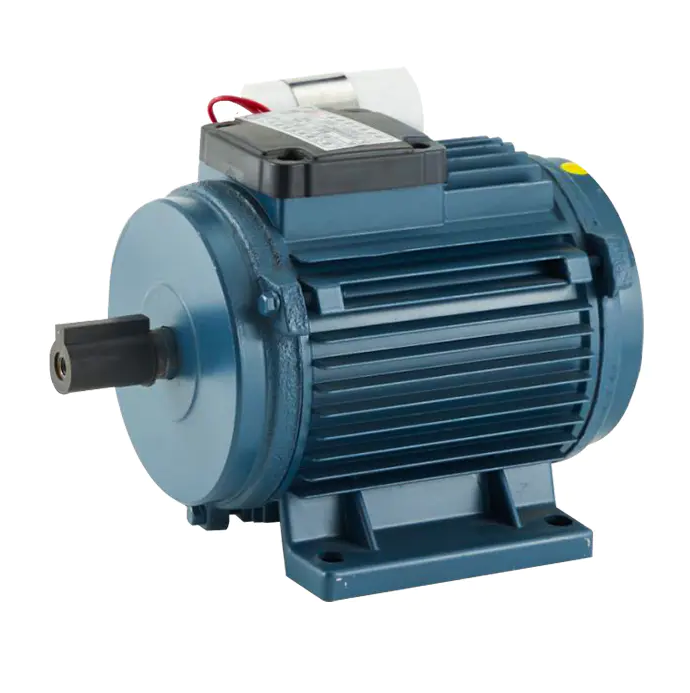

In industrial environments, matching the right motor to the task affects both performance and operational costs. Two widely used types are the asynchronous three phase motor and the permanent synchronous motor, each suited to different operational priorities and environmental conditions.
For systems with repetitive motion and predictable load patterns — such as conveyor belts in manufacturing plants — the asynchronous three phase motor provides a strong balance of performance and reliability. Its design allows it to start under load without complex control strategies, and its compatibility with standard frequency inverters gives engineers flexibility in adapting production speeds.
Conversely, the permanent synchronous motor offers advantages when applications require consistent speed and tighter regulation. Examples include precision handling in robotics, textile machinery where fabric quality depends on stable motion, or advanced packaging lines where synchronization with sensors and actuators is essential.
At Zhejiang Hechao Motor Co., Ltd., product development considers not only power and control features but also environmental challenges such as temperature variation, vibration, and duty cycles. The company’s motors are designed to integrate smoothly into existing automation frameworks and support enhanced energy utilization.
When specifying motors, understanding the interaction between load characteristics, control systems, and operational goals helps teams avoid underperforming or over-engineered solutions. Comprehensive evaluation ensures that the selected motor supports both productivity and equipment longevity.
- Art
- Crafts
- Dance
- Wellness
- Movie & Television
- Adult Entertainment
- Fitness
- Food
- Jeux
- Gardening
- Health
- Domicile
- Literature
- Music
- Business & Finance
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Drinks
- Autre